Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a set of cloud computing services offered by Google. GCP is a public platform that offers IT resources, such as storage, compute, database, Big Data, application development tools, networking, and more. The GCP services run on the same cloud infrastructure that Google internally uses to run its end-user products, such as Google Photos, Gmail, Google Search, Google Drive, YouTube, etc. Software engineers, IT professionals, and cloud administrators can access the services provided by Google Cloud Platform over a dedicated network connection or the Internet. Since 2008, Google Cloud Platform has been one of the leading cloud providers in the cloud computing field. Google has always been at top among its competitors by offering the most reliable and highly scalable platform for building, deploying, and testing real-time application environments.
A network port is a virtual point where connections end and start. Ports are software-based and managed by a computer’s operating system. Ports are standardized across all network-connected devices, with each port assigned a number, called port number. Each port in a server is associated with a specific service or process in a server. The term open port is used in a server to represent virtual points that are configured to accept packets, such as UDP, TCP, etc. In contrast, a port that rejects connections or ignores all packets directed towards it is known as a closed port. In this tutorial, we will learn the steps to open and close server ports for remote access in Google Cloud using the Google Cloud Console.
Open Server Ports for Remote Access
>> Note: Making the AWS application’s network ports public is a significant security risk. We strongly advise only allowing access to those ports from trusted networks. Suppose users need to access applications outside of a trusted network for development purposes, do not allow access to those ports using a public IP address. Instead, use a reliable and secure channel such as an SSH tunnel or a VPN.
Google Cloud servers have a few or all of their ports closed to secure them against external attacks by default. In some cases, ports needed for specific applications to operate correctly are also left open by default in Google Cloud.
If users need to access their server remotely, they must first open the necessary port(s) using the Google Cloud Console.
Using the Google Cloud Console
In order to open ports other than the default ones in Google Cloud using the Console, follow the below steps:
- First, log in to the Google Cloud Console using the Google account associated with the user’s project as an admin user.
- Go to the Compute Engine section and select the VM instances option to choose the instance for which the user wants to allow remote connections. Click on it to access the VM instance details screen.
- Next, click the View Details button in the Network interfaces section. It will open the Network interface details screen.
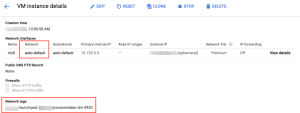
- In the left-side menu, click the VPC network option and select Firewall rules.
- Create a new firewall rule for the user’s network on the resulting page by clicking the Create firewall rule button.
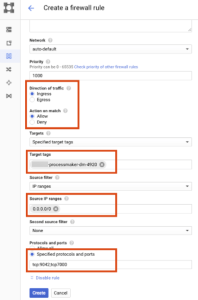
- On the next page, enter details for the new firewall rule using the below guidelines:
6.1) Name: Mention a human-readable name that makes it easy to identify the rule in this field.
6.2) (optional) Description: Enter a brief summary of the firewall rule.
6.3) Network: Select the network used by the user server in this field. Users can obtain it either from the VM instance details screen or from the Network interface details screen.
6.4) Direction of traffic: Choose the Ingress option in this field.
6.5) Action on the match: Select the Allow option in this field.
6.6) Targets: Choose the Specified target tags option in this field.
6.7) Target tags: Enter the target of this firewall rule in this field. In this tutorial, we are specifying the target that matches the instance name tag.
6.8) Source filter: Choose the IP ranges option in this field.
6.9) Source IP ranges: In order to access from anywhere, enter 0.0.0.0/0 or specify an IP address range in this field.
6.10) Specified protocols or ports: Enter the port numbers prefixed by the service in this field. Users can use commas to separate multiple port numbers and semi-colons between protocol blocks, such as tcp:80, 443; udp:8001.
For example, the image below will set up a firewall rule for Apache Cassandra on TCP ports 9042 and 7000.
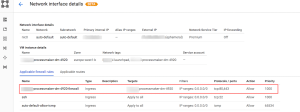
- Then, click the Create button to save the firewall rule. The new firewall rule will come into effect immediately. Users can view this new firewall rule in the Applicable firewall rules section of the instance’s Network interface details screen as shown below:
Troubleshoot:
In case if the firewall rule does not appear in the list, users can manually add the firewall rule to their instance. To do so, follow the below steps:
- Go to the “M instance details screen and click the Edit button.
- In the Network tags section, add the Target tag that the users entered when creating the rule. In this tutorial, it is the same as the instance name tag:
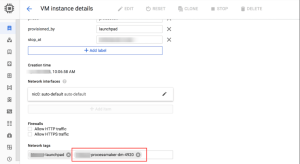
- Finally, click the Save button to make the changes take effect.
Close Server Ports and Deny Remote Access
In order to close server ports and deny remote access on that port in Google Cloud using the Google Cloud Console, follow the below steps:
- First, log in to the Google Cloud Console using the Google account associated with their project as an admin user.
- Select the Networking section and choose VPC network >> Firewall rules menu.
- Find the firewall rule(s) for the port(s) that the user wishes to close. Select each rule and then click the Delete button at the top of the page. The change comes into effect immediately.

Conclusion
This tutorial presents the steps to open and close server ports for remote access in Google Cloud via the Console. Hope this tutorial was helpful, and do reach out to us if you have any queries or suggestions.