OpenStack is a cloud Operating System used to control the deep pools of computing, networking, and storage resources within a data center. OpenStack is a free, open-source cloud computing platform. OpenStack is primarily used and implemented as an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) for cloud computing.
OpenStack is a software platform that uses multiple virtual resources to manage and create a public and private cloud. OpenStack’s default cloud-related services are storage, networking, identity, image services, etc. Users can handle the services offered by OpenStack via command-line tools, RESTful API, or a web-based dashboard. In addition, OpenStack manages many virtual machines that allow users to reduce the usage of physical resources.
Basic Principles of OpenStack
- Open Source: OpenStack is coded and published under the Apache 2.0 license. Apache allows businesses to use OpenStack for free.
- Open Design: The development group of OpenStack holds a Design Submit every six months for the forthcoming update.
- Open Development: The developers maintain an easily accessible source code repository. OpenStack provides transparent and open documentation for the community.
Components of OpenStack
Some of the significant components of OpenStack are:
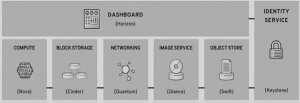
Object Storage (Swift):
The Swift component helps retrieve and store arbitrary data, such as objects, files, backups, videos, images, virtual machines, and other unstructured data in the cloud. Developers may use a unique identifier for referring the objects and files in place of the path, which directs to a file and allows OpenStack to manage where to store the files.
Compute (Nova):
Nova is a controller that helps manage services and products in virtualized environments. Compute handles many virtual machines and other instances that perform computing tasks.
Networking (Quantum):
OpenStack uses the quantum component for networking purposes. It manages all the network-related queries, such as routers, subnets, IP address management, VPNs, firewalls, and more. In addition, quantum confirms that all the other components are well connected with the OpenStack.
Block Storage (Cinder):
Cinder works traditionally attaching and detaching an external hard drive to the Operating System for its local use. It manages to add, create, and remove new disk space in the server. In addition, the block storage component offers virtual storage for the virtual machines in the system.
Dashboard (Horizon):
The dashboard is the first component that the customer sees in the OpenStack. The other backend services offered by OpenStack can be accessed using the Horizon (web user interface). Developers can access OpenStack’s components using individual API (Application programming interface). However, the system administrators use the dashboard to check and manage services in the cloud.
Image Service (Glance):
This component is used to offer image services to OpenStack. In OpenStack, image service means the virtual copies or images of hard disks. When a user plans to deploy a new virtual machine instance, they can use these images as templates with the help of this component. In addition, glance allows VMware (VMDK, OVF), virtual box (VDI), KVM (qcow2), Raw, and Hyper-V (VHD) virtual images.
Identity Service (Keystone):
In OpenStack, Keystone is the central repository that stores the key information about the users and their permissions. The Keystone component is used to manage identity services like authentication, authorization, token-based systems, AWS Styles (Amazon Web Services) logins, and other credentials (username & password).
Some of the other components available in OpenStack are:
Elastic Map-reduce (Sahara):
This component offers a simple method to the users to pre-plan Hadoop clusters by suggesting multiple options such as the cluster topology and hardware details of nodes, Hadoop version, and some more.
Orchestration (Heat):
The heat component allows the developers to store the cloud application’s necessities as files to make sure all the essential resources are available in handy. The heat component organizes many complex cloud applications through the templates via Query API and local OpenStack REST API.
Telemetry (Ceilometer):
In OpenStack, this component is used to meter and report the resource usage to its customers. So basically, Telemetry offers billing services to OpenStack’s users.
Shared File System (Manila):
Manila offers file storage for a virtual machine in OpenStack. This component gives an infrastructure for provisioning and managing shared files.
OpenStack Vs Amazon Web Services (AWS)
The difference between OpenStack and AWS usually depends on the customer’s specific requirements. Some of the differences between OpenStack and AWS are:
| OpenStack | AWS |
| OpenStack is categorized as an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Cloud Management Platform. | Amazon Web Services (AWS) is categorized as a Cloud PaaS (Platform as a Service).
|
| The images are handled by Glance (Image Service) | In AWS, images are handled by AMI (Amazon Machine Image).q |
| LBaaS handles the Load balancing traffic in OpenStack. | In AWS, the Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) automatically distributes incoming traffic from the services to the EC2 instances. |
| Serverless frameworks are not available in OpenStack. | AWS offers Serverless frameworks (Lambda). |
| OpenStack does not offer any speech or voice recognition solutions. | Lex is used for voice or speech recognition in AWS. |
| Keystone handles user authentication in OpenStack. | Identity and Access Management (IAM) handles the user authentication in AWS. |
Conclusion
This tutorial presents the history, principles, and components of OpenStack. Hopefully, it would help developers better decide about picking OpenStack for their business.